KVM Network Bridging
27 Feb 2012As many other hypervisors, KVM provide several types of networking. KVM use NAT in default, in which case the guest can reach the outside world (the host and all place the host can reach) but the outside world cannot reach the guest. That means, if you don’t need to access the guest through network (SSH for example), NAT is good enough for you. However, if you want more, let me introduce you the bridging way.
Concept
In a typical bridged network environment, all guest are connected to a virtual bridge. A host network interface is also connected to the bridge. The packets are forwarded to the guests based on their MAC address, just like any other bridges. In more detai, each guest has a corresponding tap device in the host. These tap devices are both connected to the bridge and the guest, as a network channel.
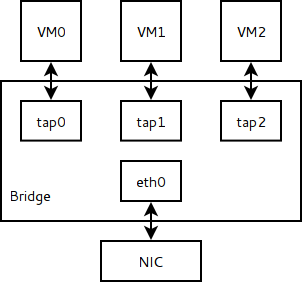
Before writing scripts and typing commands, install some tools we need: ip, brctl and tunctl. In ArchLinux, install the following packages:
pacman -S --need iproute2 bridge-utils uml_utilitiesCreate a bridge
Create a bridge is not just as simple as brctl addbr br0, some extra configurations must be done.
#!/bin/bash
addr="192.168.1.50/24"
gw="192.168.1.1"
echo "remove ip from eth0"
sudo ip addr del $addr dev eth0
sudo ip link set eth0 up
echo "create br0"
sudo brctl addbr br0
echo "add eth0 to br0"
sudo brctl addif br0 eth0
echo "bring up br0"
sudo ip addr add $addr dev br0
sudo ip link set br0 up
echo "set default gateway"
sudo ip route add default via $gw dev br0And in contrast to creating a bridge, the opposite operation is to delete it.
#!/bin/bash
addr="192.168.1.50/24"
gw="192.168.1.1"
echo "shut down br0"
sudo ip link set br0 down
echo "remove eth0 from br0"
sudo brctl delif br0 eth0
echo "remove br0"
sudo brctl delbr br0
echo "bring up eth0"
sudo ip addr add $addr dev eth0
sudo ip link set eth0 up
echo "set default gateway"
sudo ip route add default via $gw dev eth0Change the addr to the host’s IP address and gw to the host’s gateway. Save the two scripts as brup and brdown.
Prepare tap config/deconfig scripts
Creating tap device is the job of qemu, what the user need to do is provide a config script and a deconfig script. The config script qemu-ifup is called when a guest starts.
#!/bin/bash
tap=$1
echo "bring up $tap"
sudo ip link set $tap up
echo "add $tap to br0"
sudo brctl addif br0 $tapThe deconfig script qemu-ifdown is called when a guest exit.
#!/bin/bash
tap=$1
echo "remove $tap from br0"
sudo brctl delif br0 $tap
echo "shut down $tap"
sudo ip link set $tap downConfig guest network
Now everything is setup, start guest with the following parameters:
qemu-kvm -hda /path/to/vm.img -net nic -net tap,script=/path/to/qemu-ifup,downscript=/path/to/qemu-ifdown
The last thing is to setup guest’s network as the same as the host but choose a unique IP address.